Translational diseases models and neurodegeneration
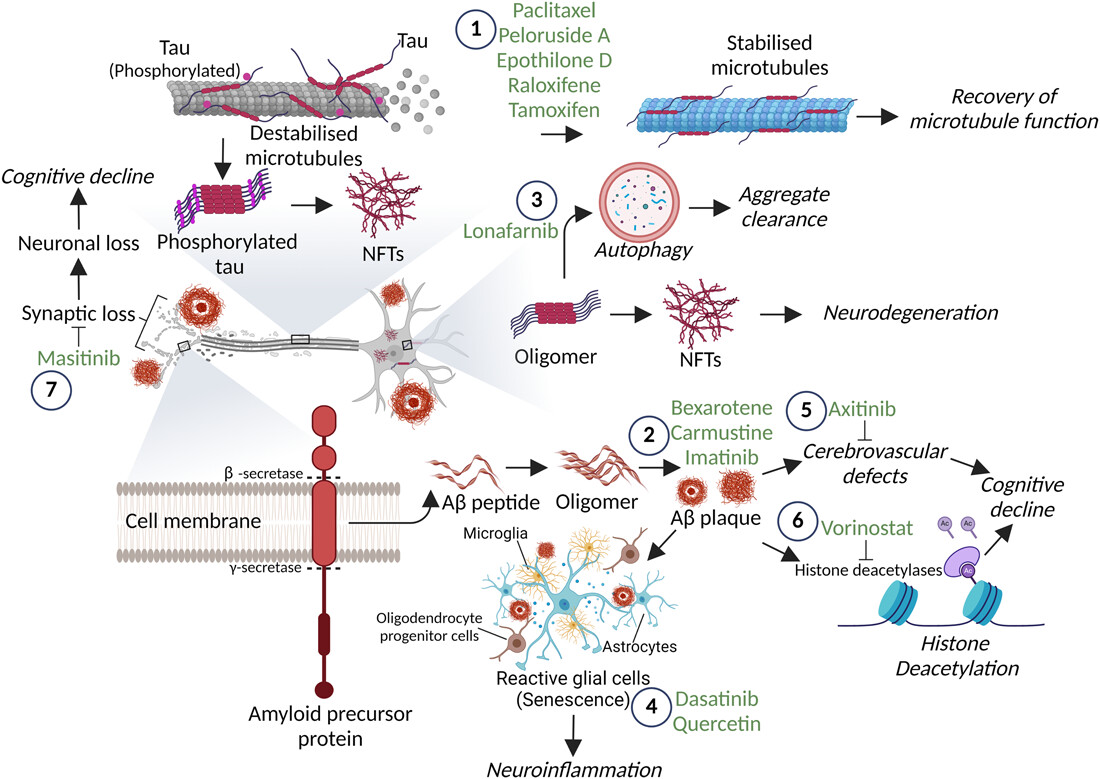
Our group, Translational Disease Models and Neurodegeneration, investigates the molecular and cellular mechanisms that drive neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and frontotemporal dementias. We study how disease-associated proteins misfold, aggregate, and spread, and how these events contribute to neuronal dysfunction and disease progression.
We aim to identify strategies that can slow or prevent these pathological processes. Our work encompasses peptide- and small–molecule–based approaches, as well as emerging technologies such as targeted protein degradation, with a focus on modulating protein aggregation, neuroinflammatory signaling, and other mechanisms central to neurodegeneration. A major emphasis is placed on linking mechanistic insights to translational applications through the development of biomarker platforms that can detect early molecular changes and support therapeutic evaluation.
We use a diverse set of experimental systems, including iPSC-derived neurons, 3D neural cultures, organoids, microfluidic co-culture platforms, and established rodent models. Together, these complementary approaches enable us to construct a comprehensive understanding of disease mechanisms and contribute to the development of effective diagnostic tools and disease-modifying therapies.
- Mechanisms of protein aggregation and spreading
We study how tau and α-synuclein aggregates form, how mutations alter their structure, and how these assemblies propagate through neural systems. - Targeted modulation of disease-driving proteins
We design and evaluate peptide inhibitors and small-molecule modulators targeting disease-defining motifs such as the VQIVYK region of tau and the NAC domain of α-synuclein, alongside BTK-centered strategies including PROTAC approaches. - Functional biomarkers for early detection
We advance seed amplification assays (RT-QuIC and IP/RT-QuIC) to detect and characterize pathological tau and α-synuclein seeds in patient samples, aiming to improve diagnostic precision and therapeutic monitoring. - Human-relevant cellular and tissue models
We employ iPSC-derived neurons, 3D neural cultures, organoids, and microfluidic BBB models to recreate disease mechanisms and evaluate therapeutic interventions in physiologically meaningful settings. - Translational pharmacology and drug repurposing
We explore kinase-driven pathways, including BTK, and assess repurposed anticancer and targeted agents for their relevance to neurodegenerative disease mechanisms.
- Peptide inhibitors targeting α-synuclein seed activity
Developing and validating NAC-focused peptide inhibitors in cellular models, patient-derived seed assays, and mouse models of synucleinopathy. - Tau mutation–sensitive inhibitor profiling
Investigating how specific tau mutations alter aggregation behavior and determining which VQIVYK-targeting agents are most effective against mutation-driven forms of tau pathology. - Seed-based biomarker platforms
Applying automated immunoprecipitation and RT-QuIC workflows to analyze α-synuclein and tau seeds from clinical samples, linking seed biology to therapeutic testing. - Advanced iPSC and 3D disease models
Building and applying iPSC-derived neuronal systems, organoids, and engineered 3D co-cultures to test aggregation, spreading, neuroinflammation, and responses to targeted therapeutics. - BTK-directed therapeutic development
Designing and evaluating BTK inhibitors and BTK-oriented PROTAC degraders, and assessing their impact on neuroinflammatory signaling and aggregation-linked pathology.
| Project: | The role of tumor hypoxia in the emergence of acquired resistance to drugs aimed at microtubules |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 1 |
| Intended for: | Doctoral training |
| Summary: | 1 place in full-time study |
| Project: | Generation of 3D human neuronal cultures: application to modeling CNS diseases |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 1 |
| Intended for: | Master training |
| Summary: | - |
| Project: | Biochemical and cellular analysis of amyloid staining agents in models of tauopathies and synucleopathies |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 1 |
| Intended for: | Master training |
| Summary: | - |
| Project: | Investigating Effects of Aggregates of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins on Microglia: Implication for Neurodegenerative Diseases |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 1 |
| Intended for: | Master training |
| Summary: | - |
| Project: | Efficacy of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Against Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 1 |
| Intended for: | Master training |
| Summary: | - |
| Project: | Systems approaches to understanding aging and neurodegeneration |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 2 |
| Intended for: | Doctoral training |
| Project: | Role of axonal transport and pathology in neurodegeneration |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 2 |
| Intended for: | Doctoral training |
| Project: | Research and development of agents for cancer, neurodegenerative and infectious diseases |
|---|---|
| Supervisors: | De Sanctis Juan Bautista Ph.D., Hajdúch Marián M.D., Ph.D., Džubák Petr M.D., Ph.D., Urban Milan Ph.D., Das Viswanath M.Sc., Ph.D. |
| Available: | 5 |
| Intended for: | Doctoral training |